KEY CONCEPTS
Earthquakes
Where do earthquakes occur?
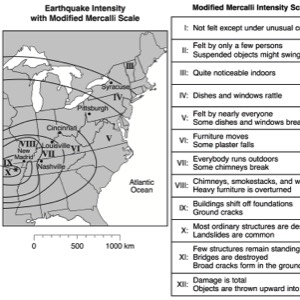
Earthquakes occur along plate boundaries where two chunks of lithosphere scrape
together. The focus is the location where the energy is released and the epicenter is location on the earth’s surface directly above the focus.
Seismic Waves
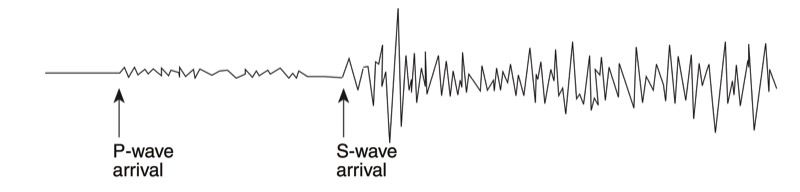
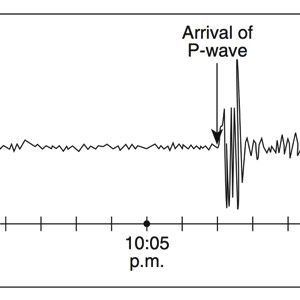
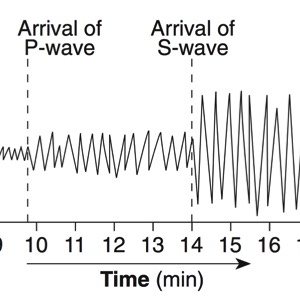
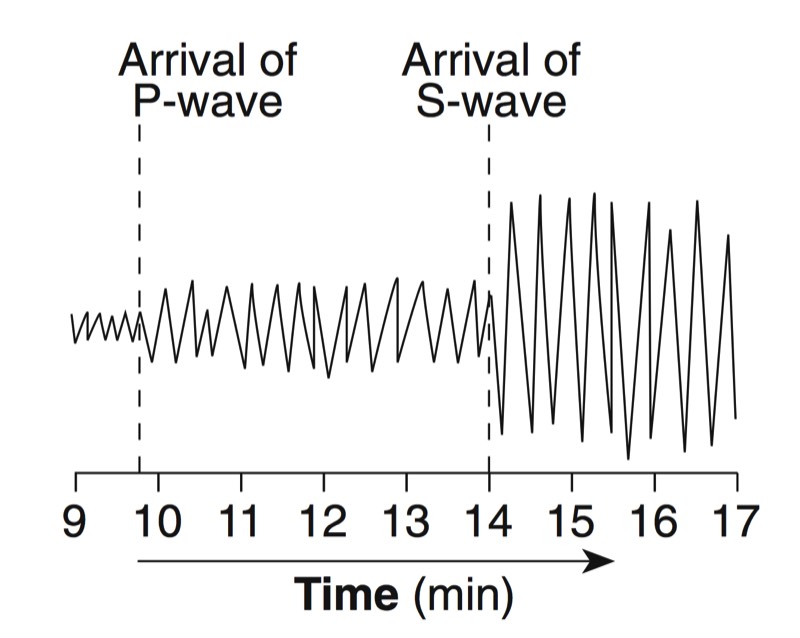
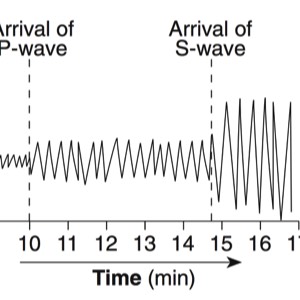
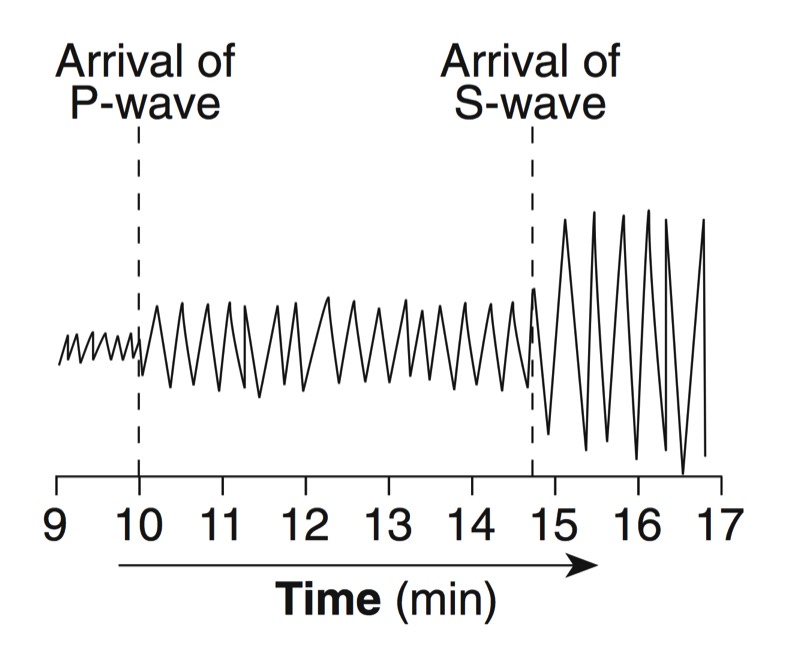
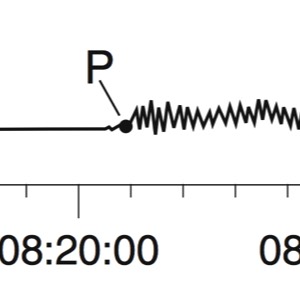
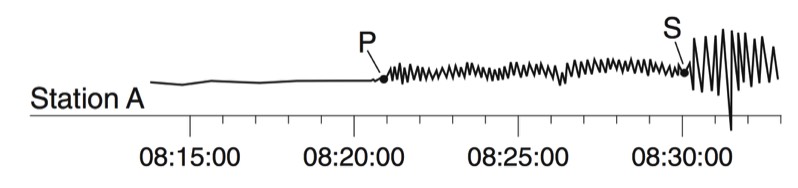
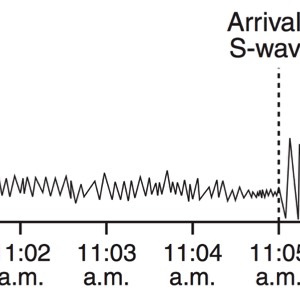
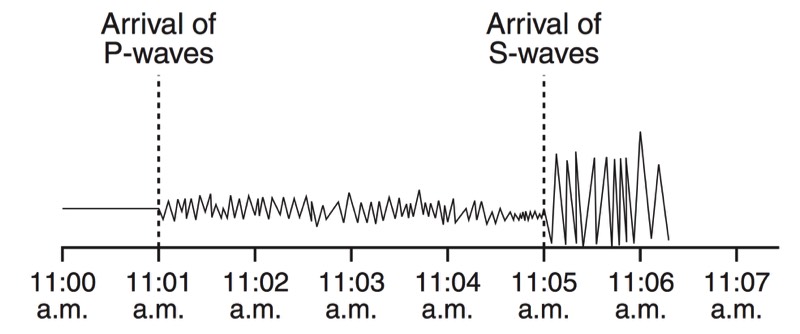
During an earthquake, several types of waves are generated. The vibrations felt are actually called seismic waves that are traveling through the Earth.
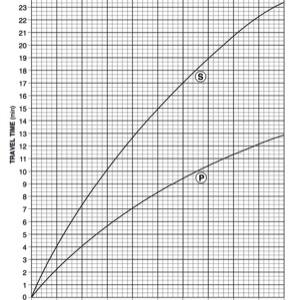
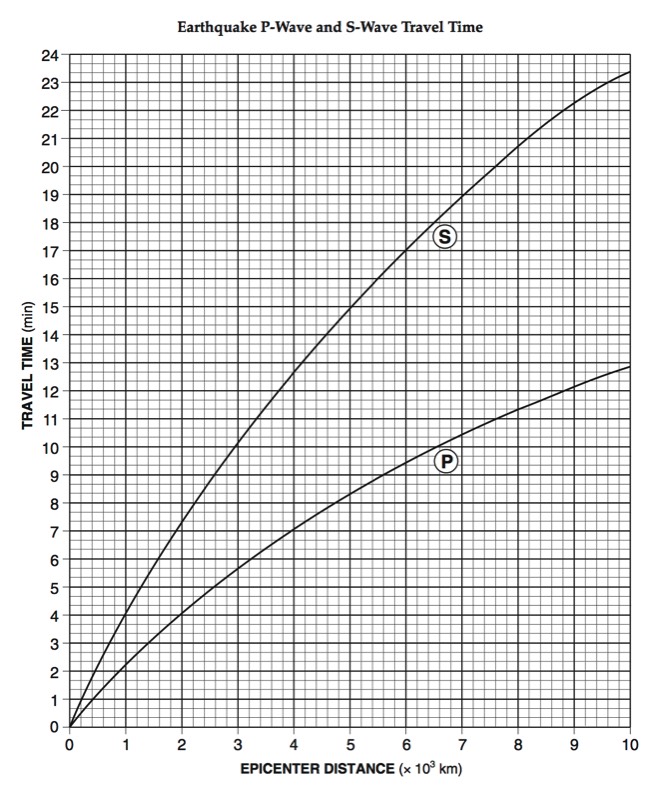
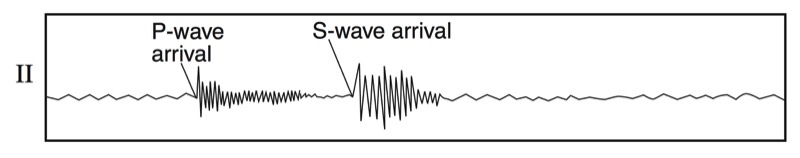
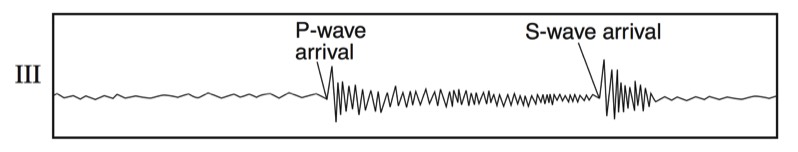
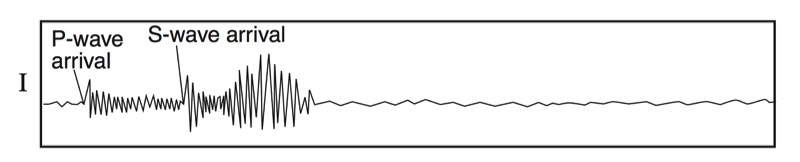
P-Waves
- Primary Wave (Compression Wave)
- Travels “phastest” so it arrives at a seismic stations “phirst”
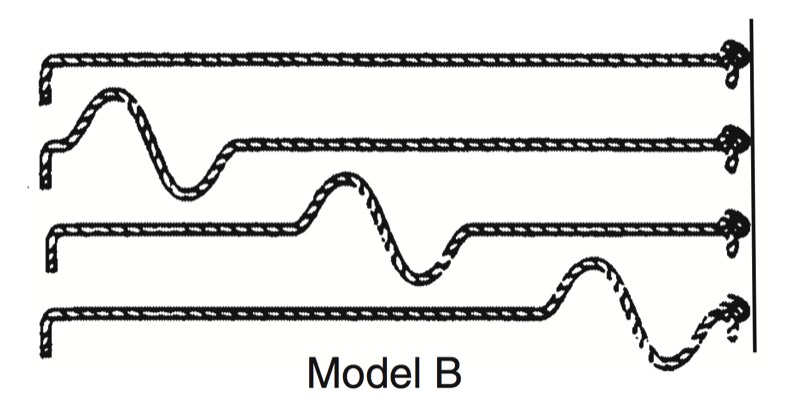
- Push-pull wave, vibrates forward and backward in the same direction that the wave travels
- Pass through solids, liquids (magma), and gasses
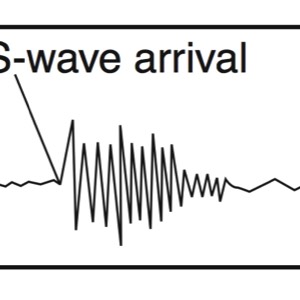
S-Waves
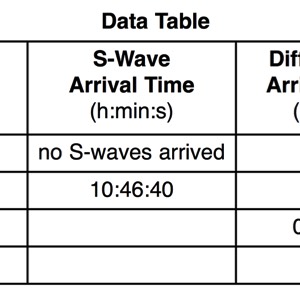
- Secondary Wave (Shear Wave)
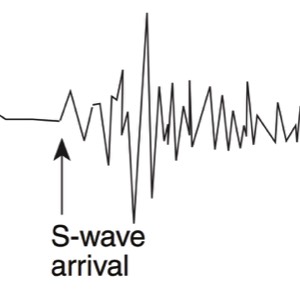
- Slow wave, not as fast as the P-wave, arrives at a seismic station second
- Shake wave, vibrates side-to-side
- Solids wave, only travels through solid layers
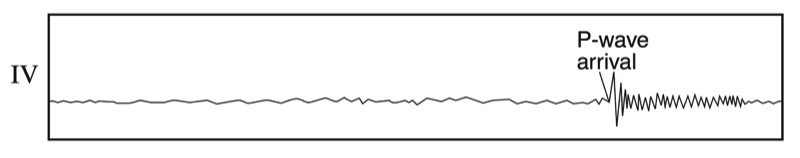
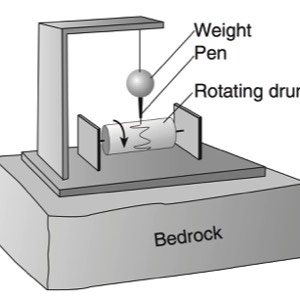
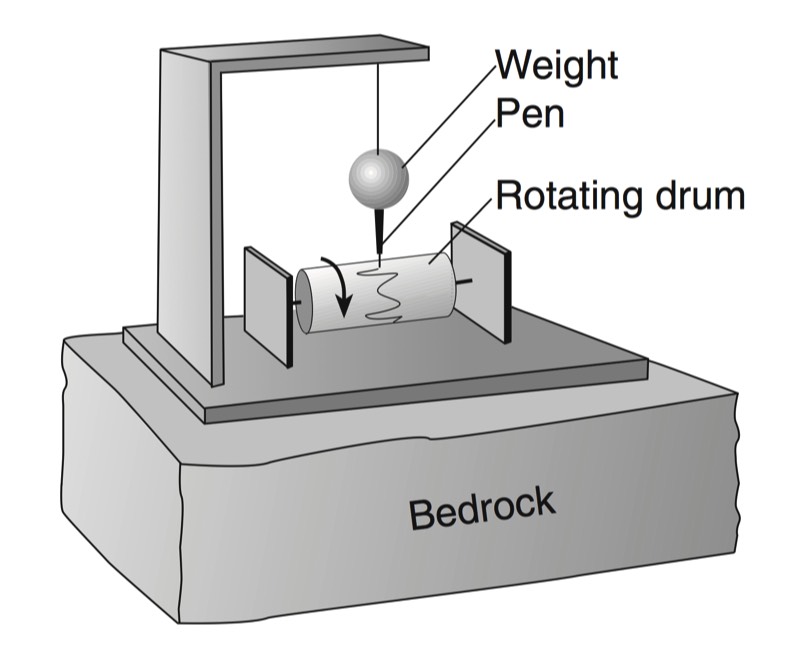
Seismographs
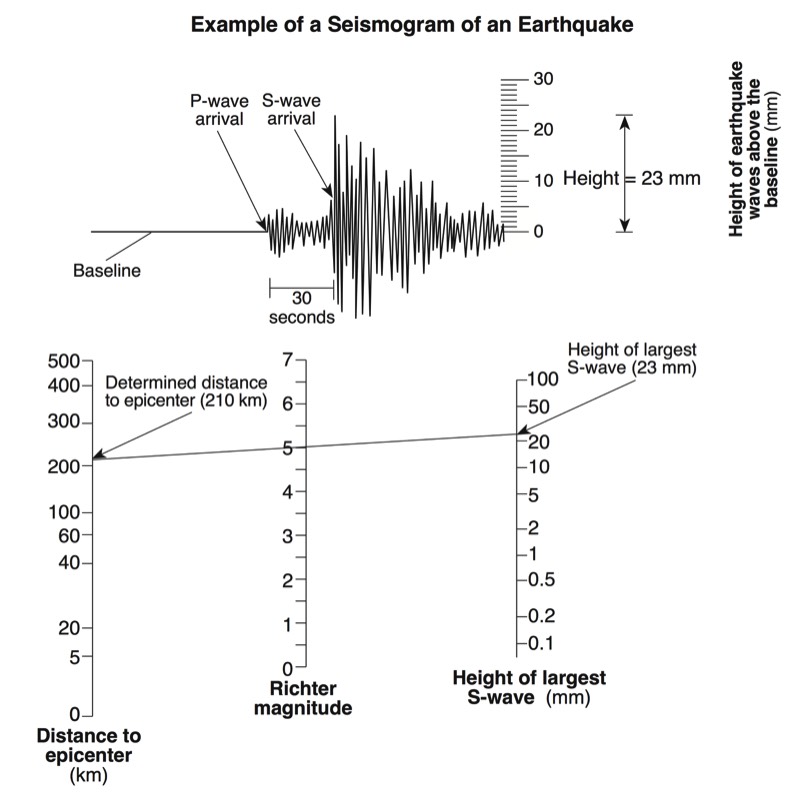
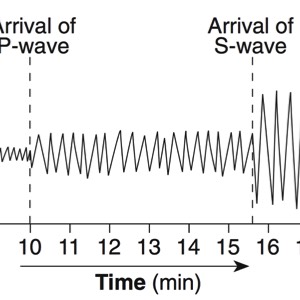
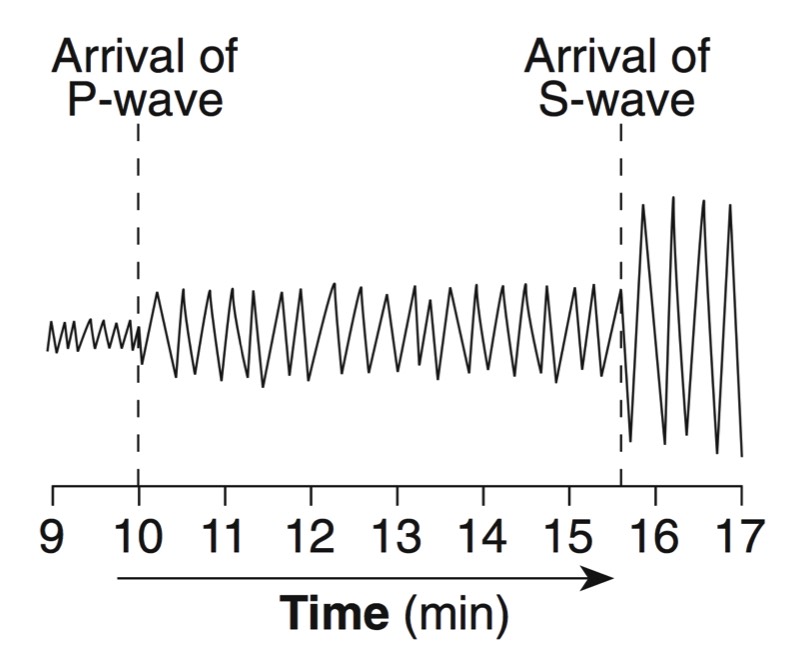
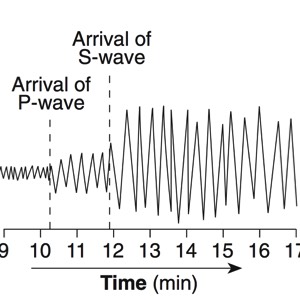
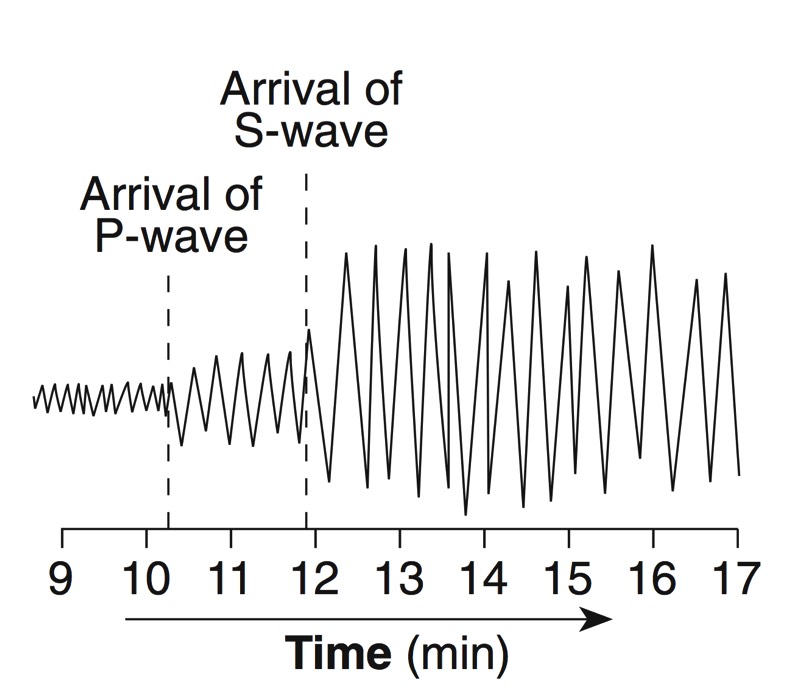
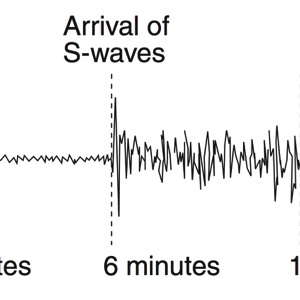
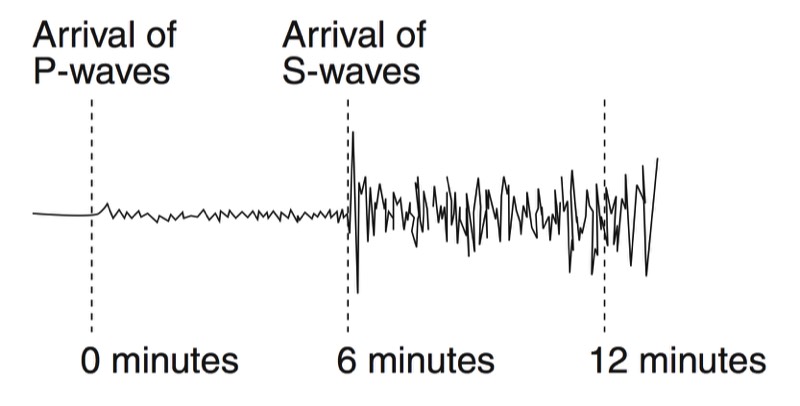
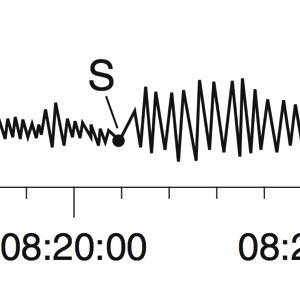
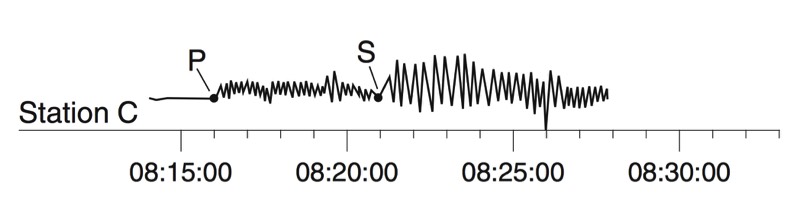
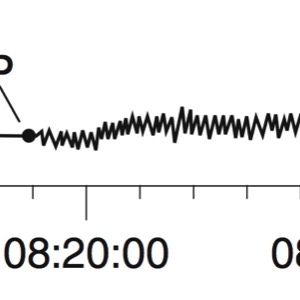
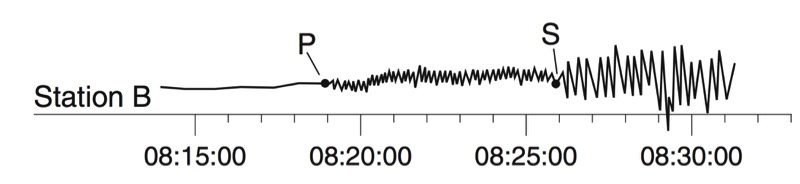
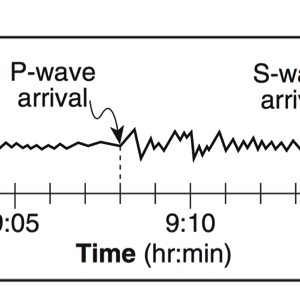
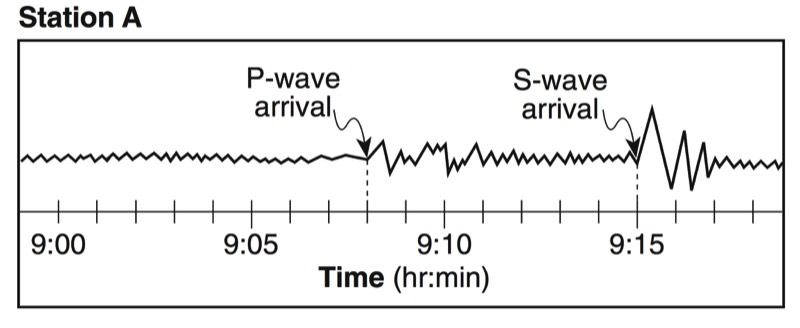
A seismograph is an instrument that detects and records seismic waves. By studying a seismogram, we can determine a seismic wave’s distance and size
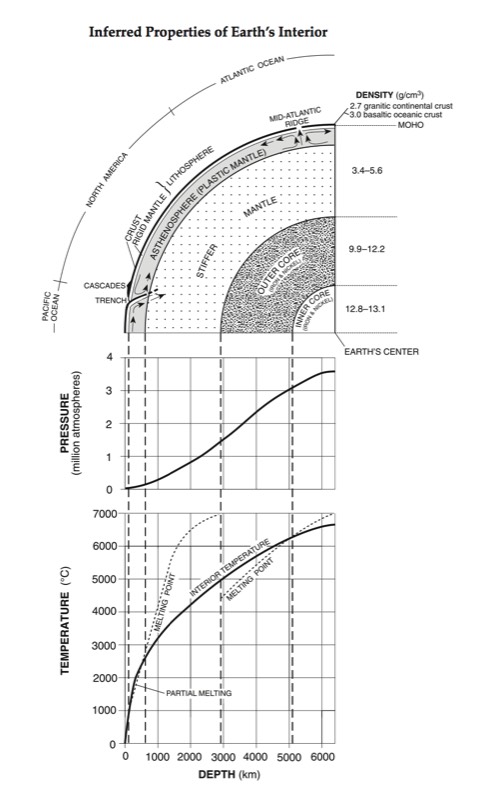
Seismic Waves Traveling Throughout the Earth
- P-Waves travel through solids, liquids, and gasses
- S-Waves travel only through solids
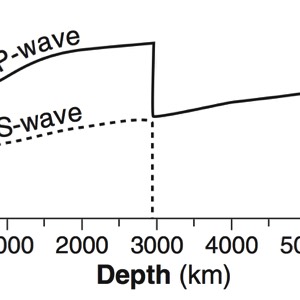
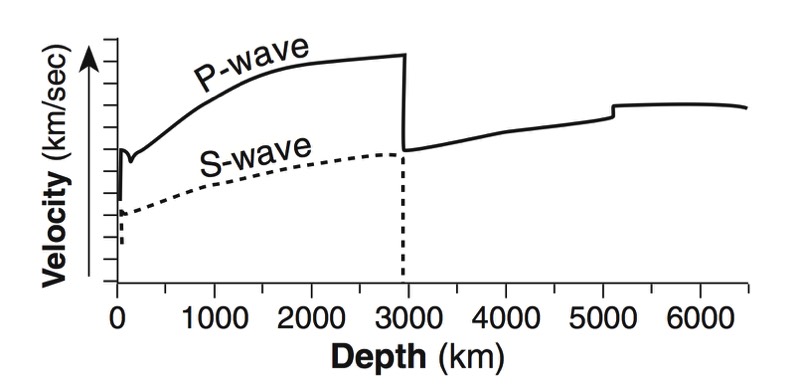
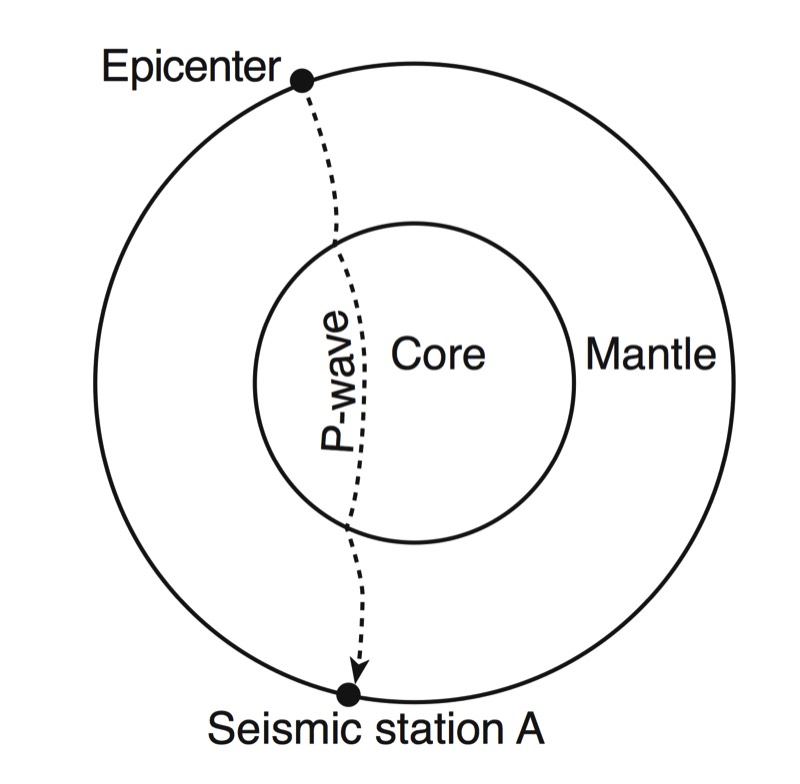
- Seismic waves travel faster through denser material.
- Because of this, the path traveled by a seismic wave is bent towards the surface.
- Properties of the material (such as density and pressure) that the waves pass through can be inferred by the speed and angle that the waves travel.
- The layers of the earth are determined by the jumps in velocity and “echoes” of seismic
waves. - The MOHO is a boundary between the crust and the upper mantle where the velocity of
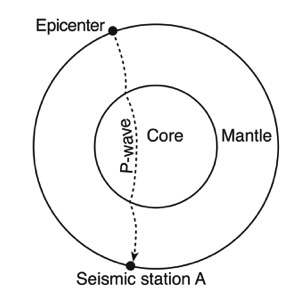
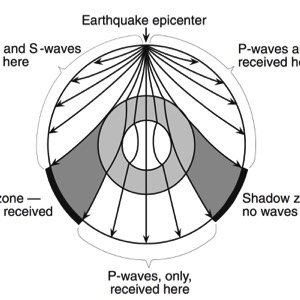
waves jumps up sharply. This sharp increase in velocity is called a discontinuity. - A shadow zone occurs on the opposite side of the earth from an earthquake because of
the liquid outer core. - S-Waves are stopped all together as they are absorbed by the liquid outer core. The P-
Waves are refracted (bent) as they change velocities in different density materials. This !creates a zone in which no waves are picked up at all.
VIDEOS
ANIMATIONS
Most of the animations found below are Flash files. These files will not function on iPads or iPhones. Viewing these animations on a computer may require updating or downloading the free Adobe Flash Player.
- Tsunami Detection
- Earthquake Focus/Epicenter
- Earthquakes
- Locating an Epicenter
- Seismic Wave Motion #1
- Seismic Wave Motion #2
- Seismic Wave Motion #3
- Seismic Waves
- Shadow Zone #1
- Shadow Zone #2
- Earthquake Depth
- Southeast Asian Tsunami
- Tsunami
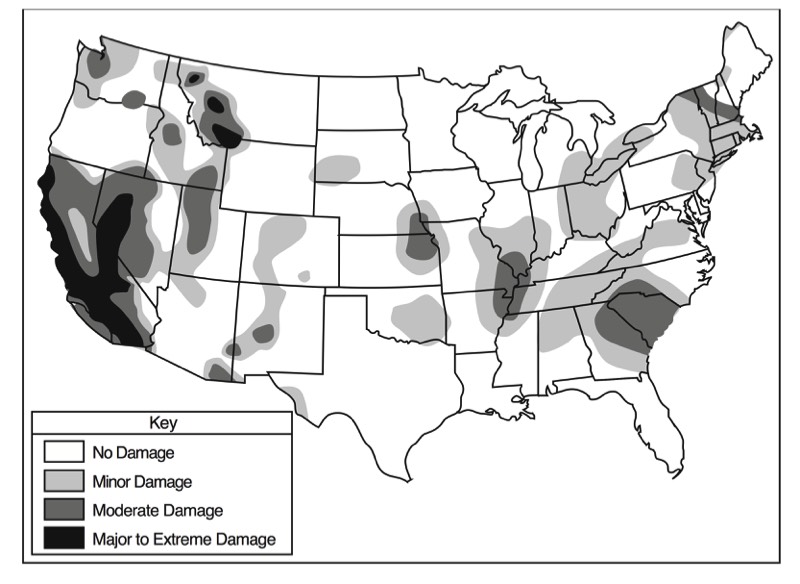
- California Earthquakes
- Earthquake Formation
- Earthquake Footage #1
- Earthquake Footage #2
- Earthquakes
- Earthquake Tutorial
- Transform Fault
- Normal Fault
- Reverse Fault
- Strike-Slip Fault
- Thrust Fault
- Seismic Waves ESRT
- P-Wave Motion
- S-Wave Motion
- Seismic Wave Refraction
- Seismometer #1
- Seismometer #2
- Seismometer #3
- Tsunami Motion
- Tsunamis
LABS
DIAGRAMS
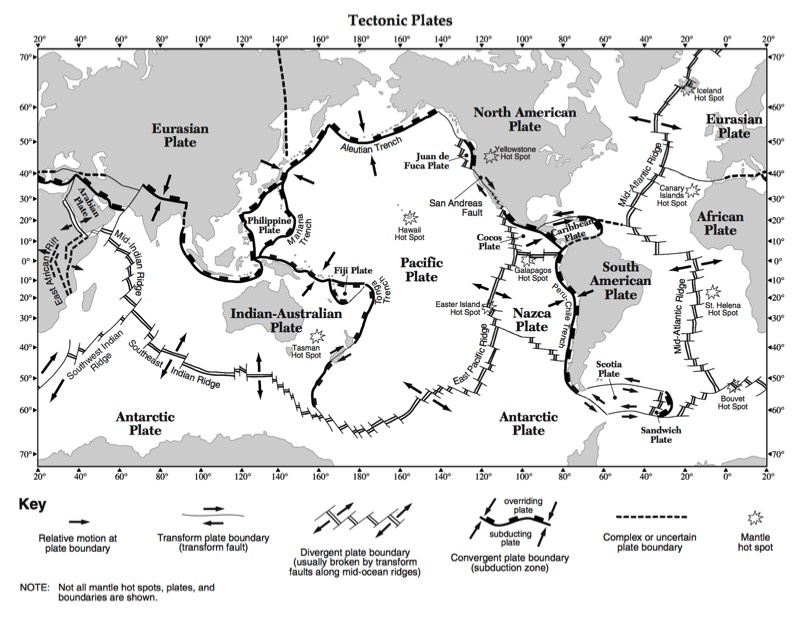
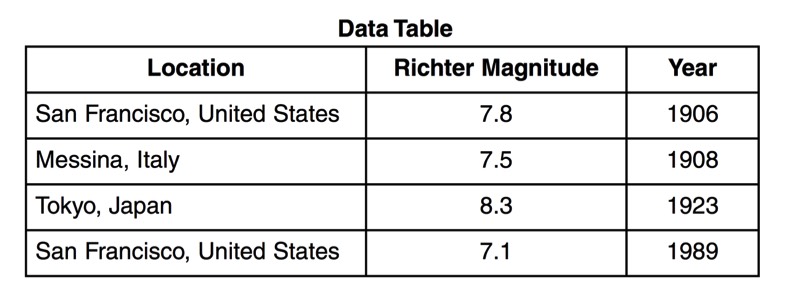
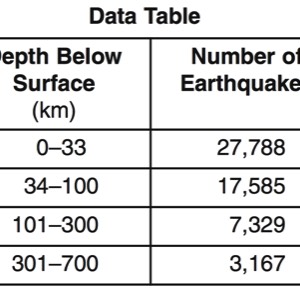
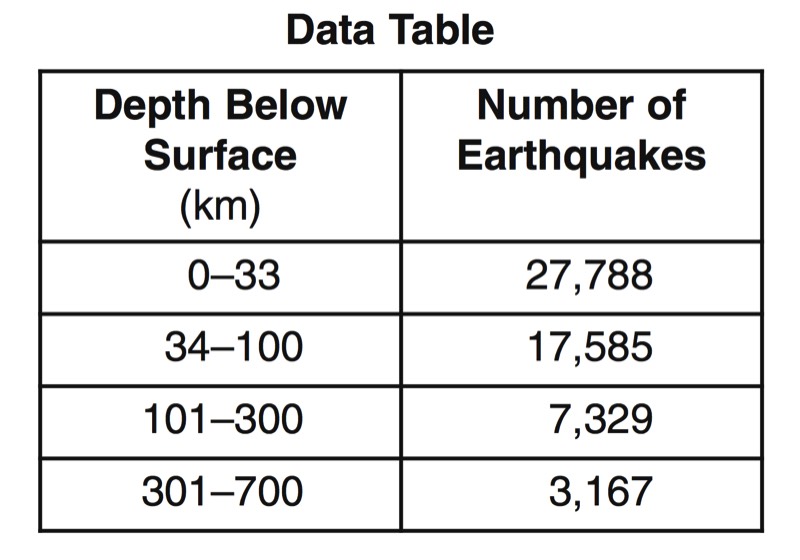
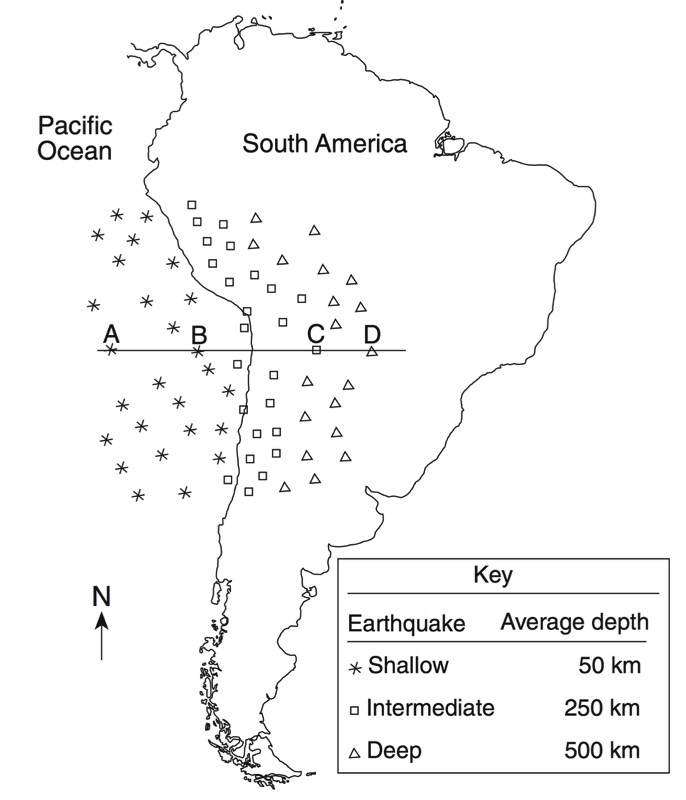
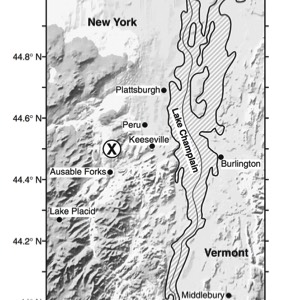
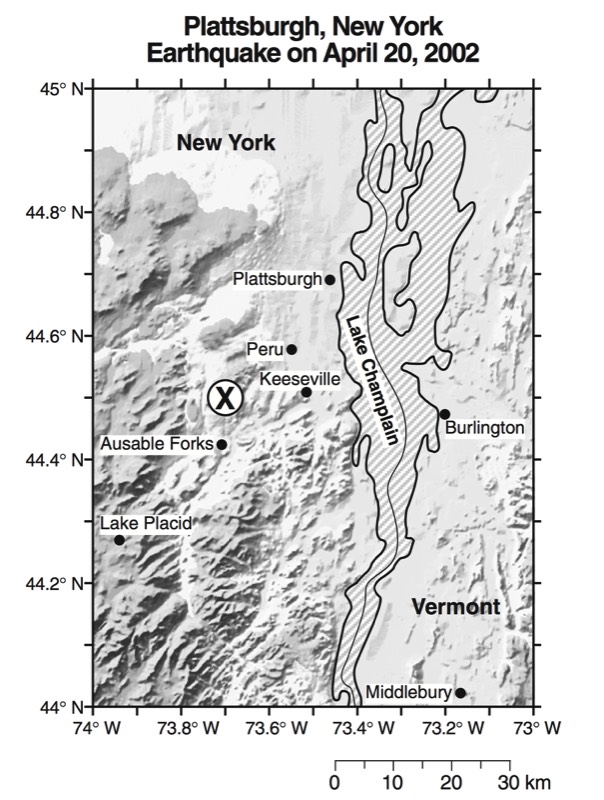
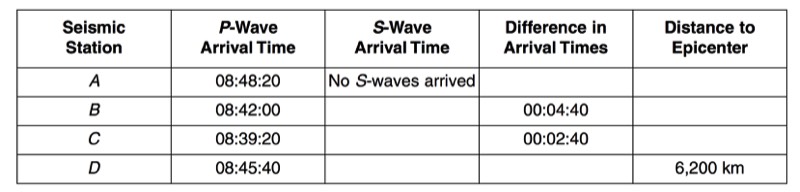
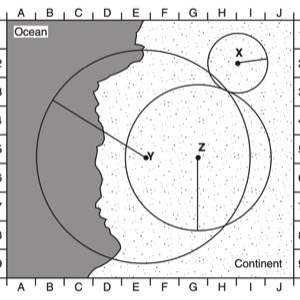
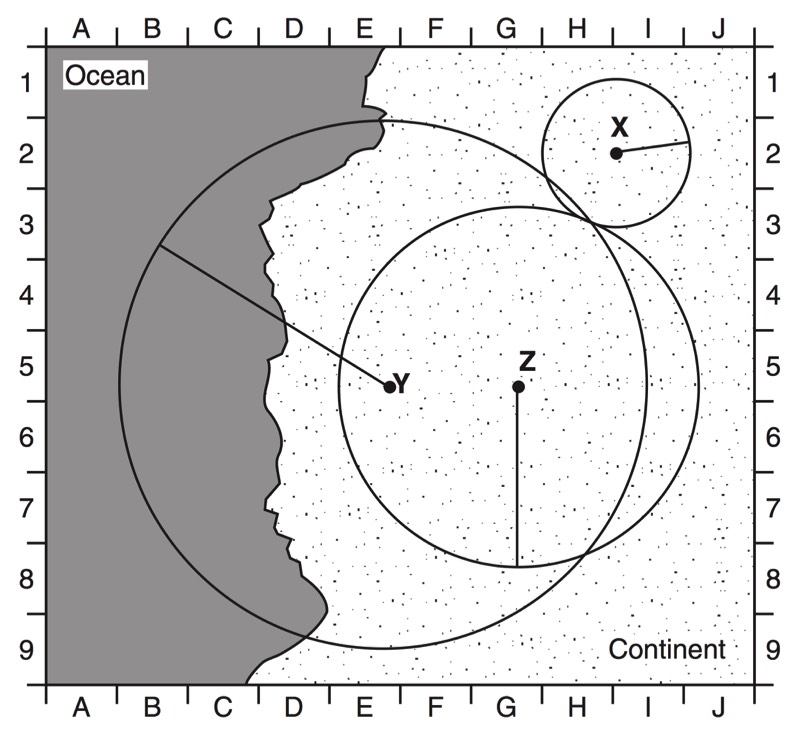
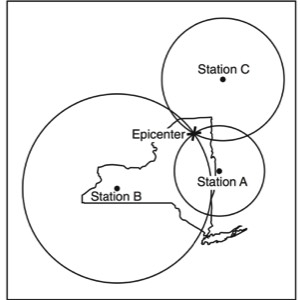
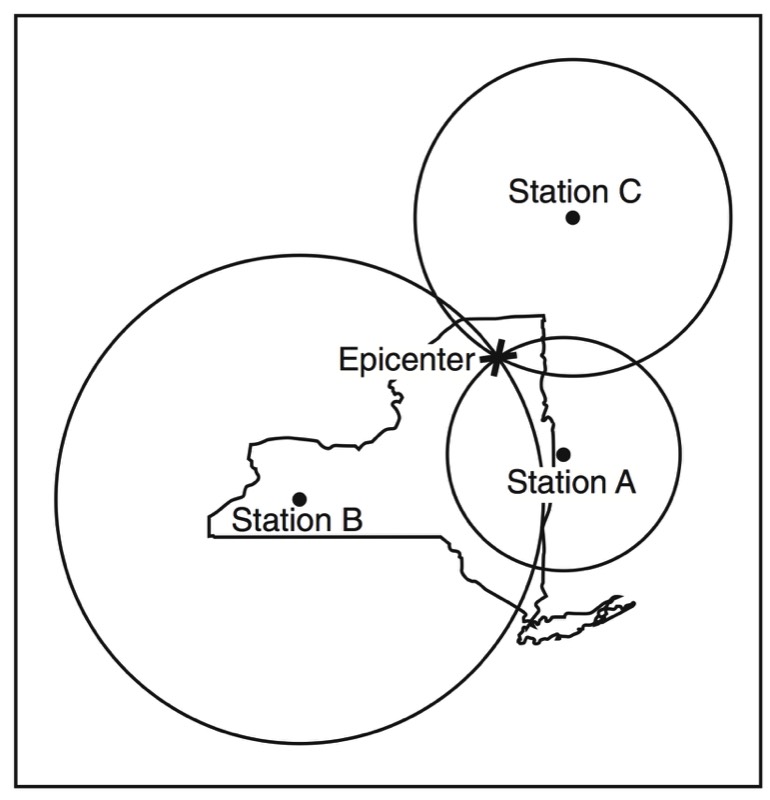
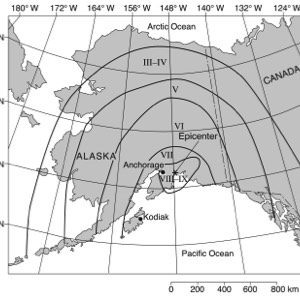
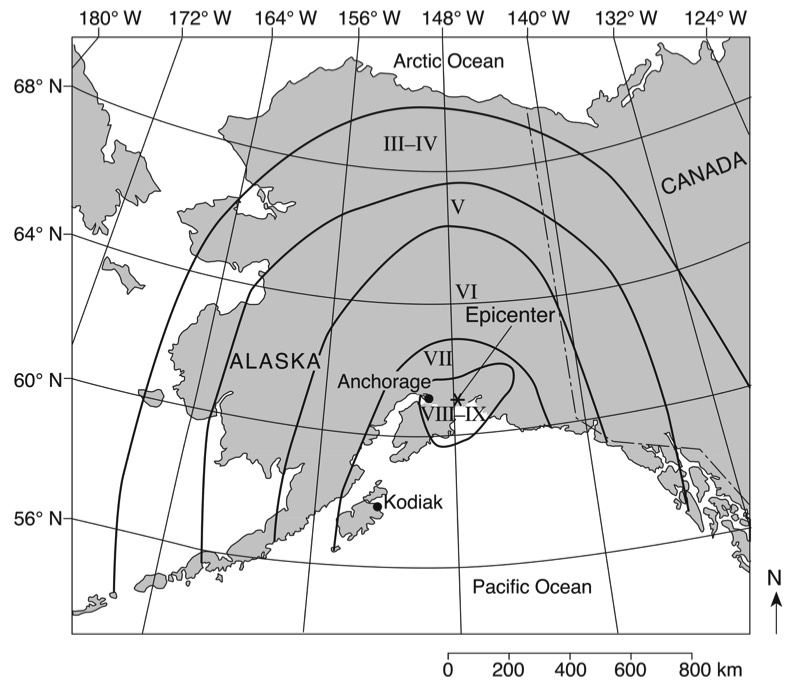
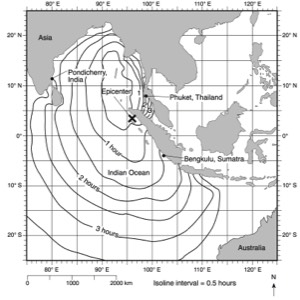
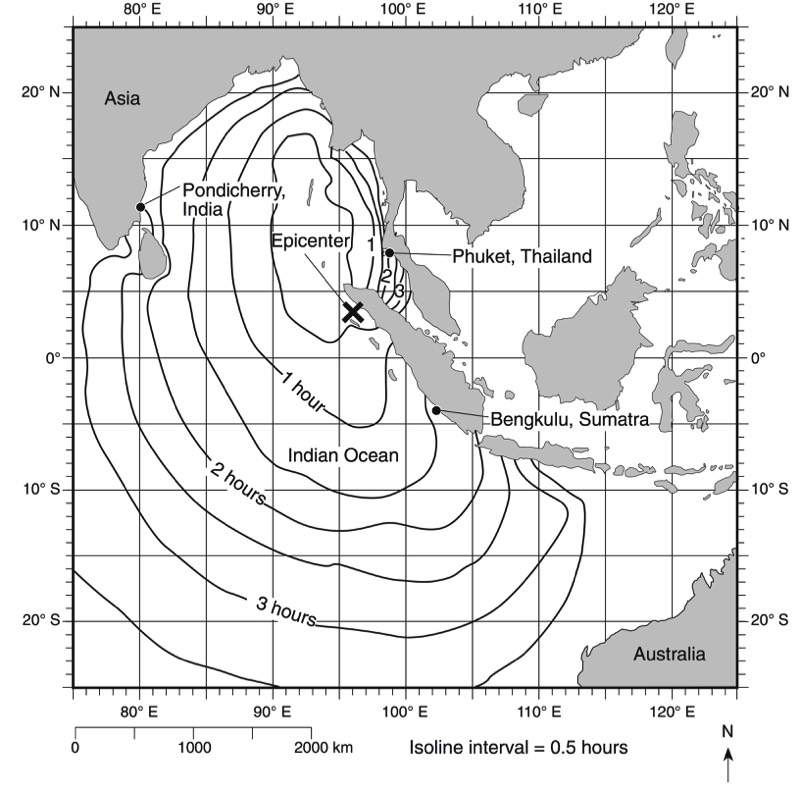
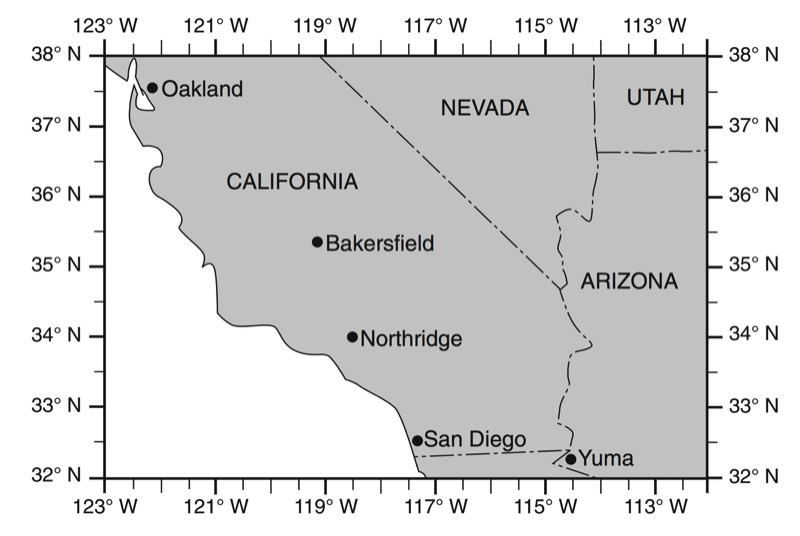
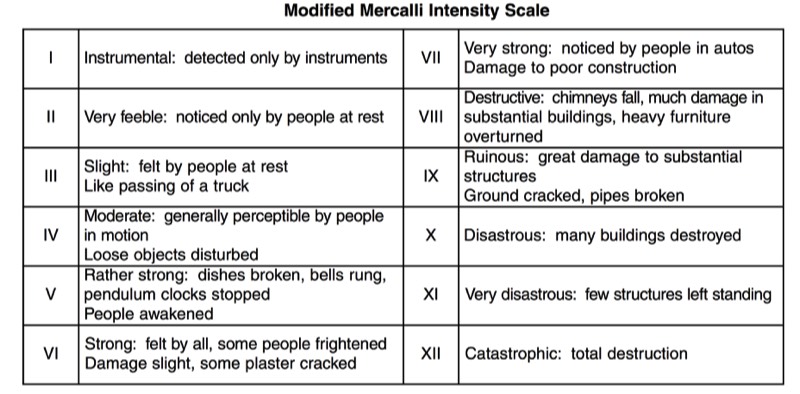




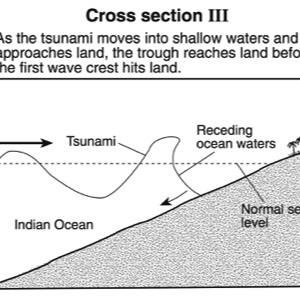
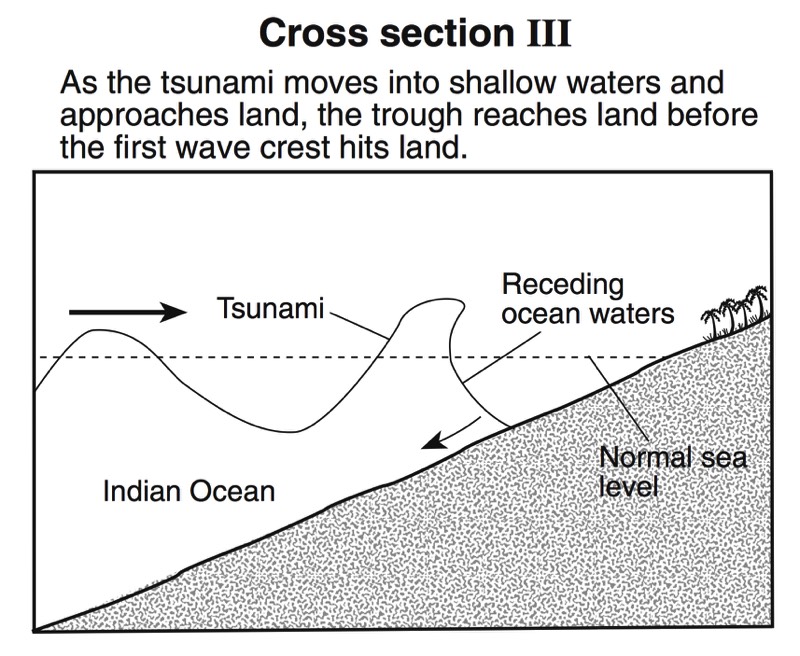
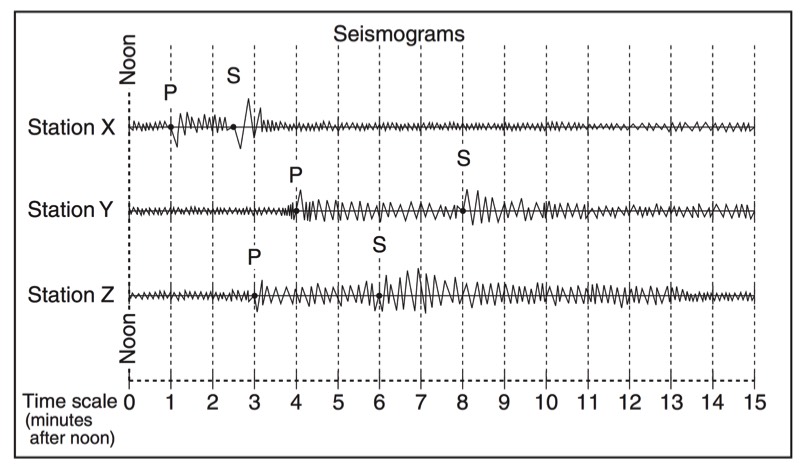
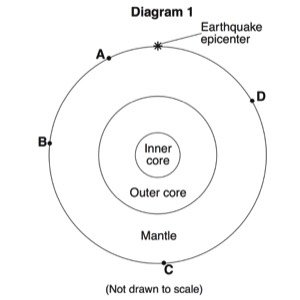
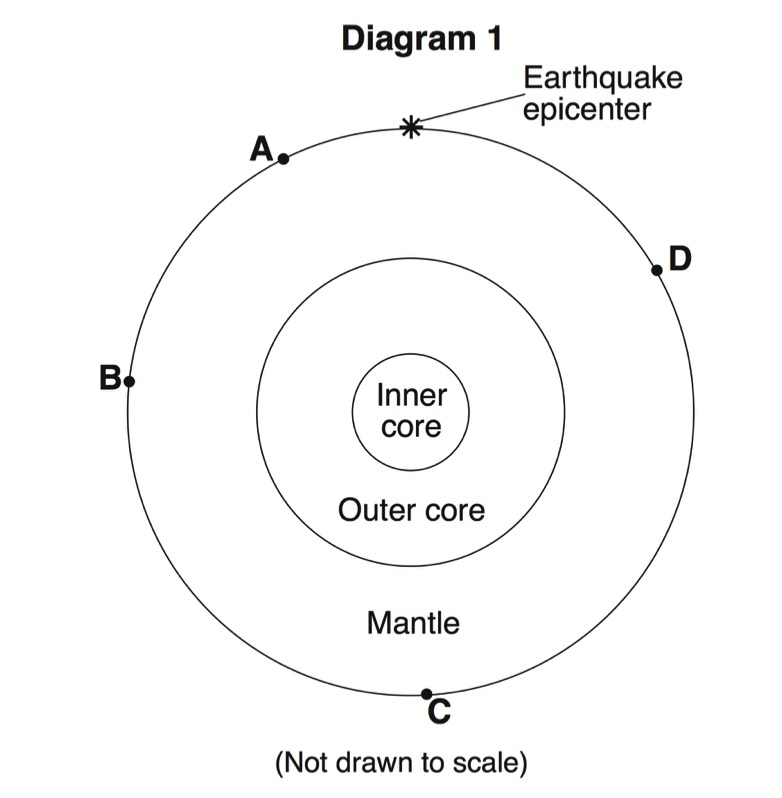
HANDOUTS
- Determining Epicenter Distance
- Determining Richter Magnitude
- Earthquake Notes
- Earthquake Online Activity
- Earthquake Practice
- Earthquake Review Sheet
- Epicenter Distance Practice
- Epicenter Location
- Finding Epicenters 3
- More Earthquake Practice
- P and S-Wave Chart Practice
- Shadow Zone Worksheet #1
- Shadow Zone Worksheet #2t
- Sumatra Tsunami Seismogram #1
- Sumatra Tsunami Seismogram #2
- Travel Time Chart
- Travel Time Curve Worksheet
- Using the P and S Wave ESRT Notes